
After critiquing data for accuracy (informally, on the ground, using the Stratton (2009) methodology, or otherwise), it is most likely that modifications will be required to reflect local knowledge of fuel models and fire behavior, recent management activities, recent wildfires, etc. Realize, however, that when modeling landscape-level fire behavior, one must accept that there will be some error in the data, but one should always strive to minimize this. It is important to document changes as well as make them incrementally, making it easier to see the effect of the changes and backtrack, if necessary.
With ArcFuels10, complex raster value replacements are easily made on the individual raster data components, rather than on the landscape file. Tools such as the FARSITE landscape calculator and the LANDFIRE Area Change Tool (LFACT) are available to make changes on the landscape file, but are generally limited to simple changes (Stratton 2009).
Within ArcFuels10, the Modify Raster Values form is available to update or correct raster data. When the form is used, a projected raster file is created and added to ArcMap. The changes can be made to either floating point or integer data. Either discrete values or ranges of values can be replaced, multiplied by, or added to. Options include making changes to the entire landscape or to selected areas using another raster to define the location. The output raster extent also need not be identical to the input data.
How the raster will be modified:
Where to apply the changes:
Output details:
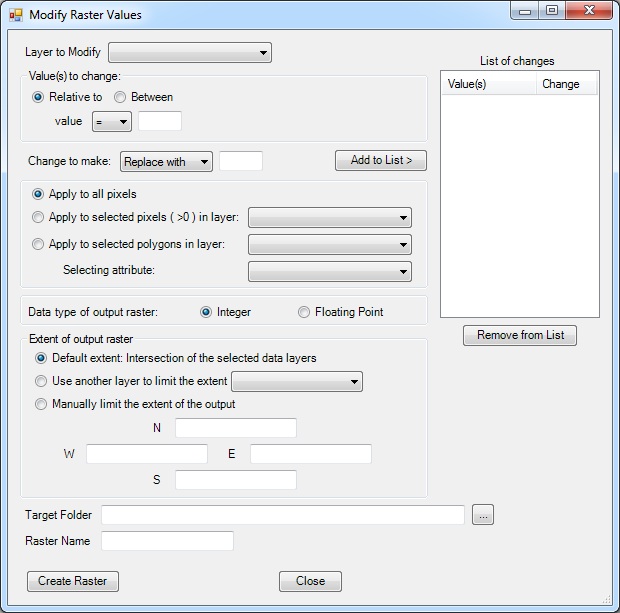
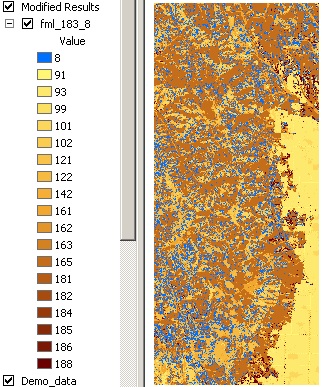
After careful review of the fuel model assignments in the LANDFIRE data, you have decided that all the fuel model 183 assignments would better be represented by a fuel model 8. You would like to apply this change across the whole landscape.
Click the Tools button on the ArcFuels10 toolbar then select Modify Raster Values from the drop-down list.

Fill out the Modify Raster Values form following the figure below.
Return to ArcMap.
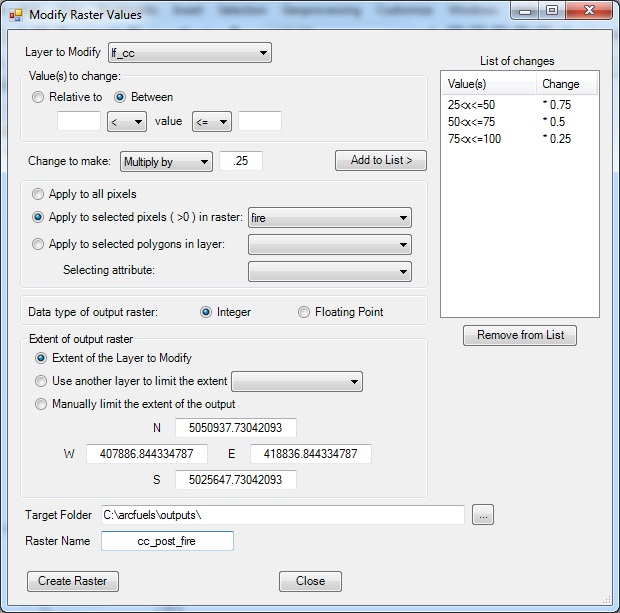
A wildfire has occurred since the raster data for your project area was created. The wildfire resulted in decreases to canopy cover. Multiplication factors will be used to adjust the canopy cover values, where pixels with higher canopy cover are reduced more than those with lower canopy cover. For areas where the pre-fire canopy cover is between 25-50% it will be reduced by 25% (multiplication factor of 0.75), 50-75% will be reduced in half (multiplication factor of 0.5), and where canopy cover is >100% it will be reduced by 75% (multiplication factor of 0.25)
You only want to modify the area within the fire, but need the output raster to be the same extent as the original data. This update will use a non-zero raster layer to define the fire area to make the changes.
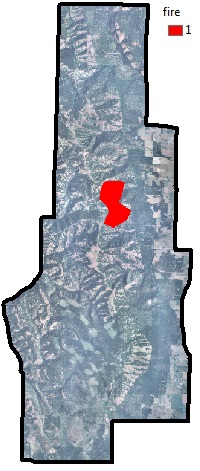
Map of the Mt. Emily project area, with the recent fire overlayed.
Click the Tools button on the ArcFuels10 toolbar then select Modify Raster Values from the drop-down list.

Fill out the Modify Raster Values form following the figure below.
Return to ArcMap.
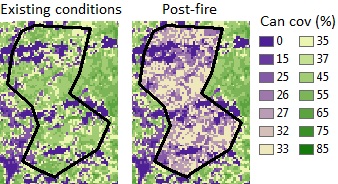
Existing conditions (A), and post-fire (B) canopy cover within the fire boundary.
In order to model the change in potential fire behavior from a pruning treatment that will lift the canopy base height you need to update your raster data to reflect the treatment. Canopy base height will be lifted by 3 m (6 ft) for all areas within your proposed treatment units where it is currently less than 6 m (18 ft). You have an attributed shapefile that specifies the polygons that will be part of the treatment with a field where the value is 1. The analysis area also changed from the original planning period, so the output raster extent will reflect the new smaller project area.
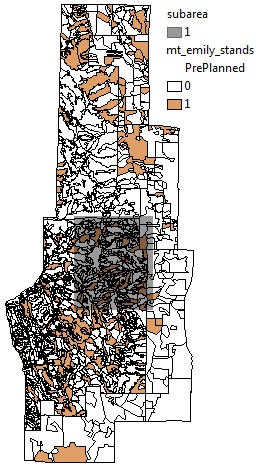
Mt. Emily stand layer with the pre-planned treatment stands (orange) and the new project sub area (gray).
Click the Tools button on the ArcFuels10 toolbar then select Modify Raster Values from the drop-down list.

Fill out the Modify Raster Values form following the figure below.
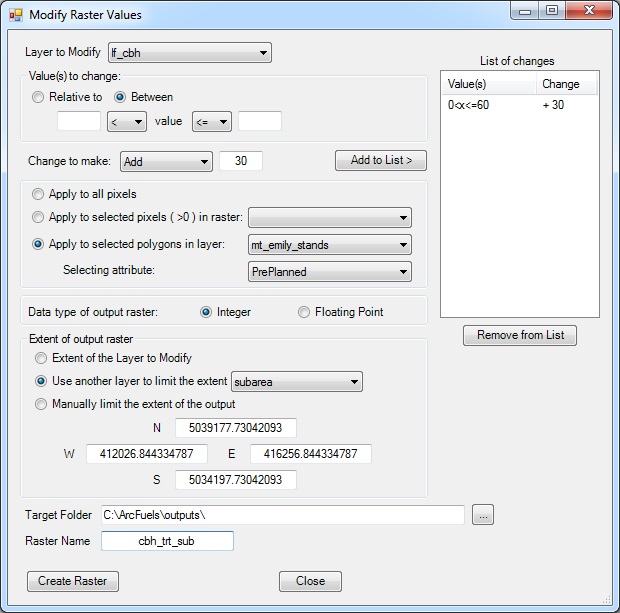
Return to ArcMap.
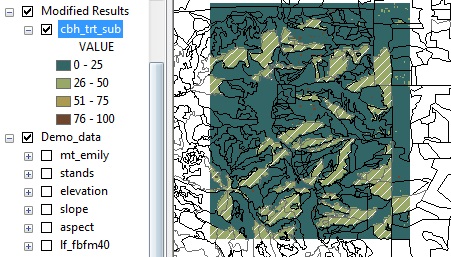
Updated canopy base height raster with the new extent. The white hashed stands are those that are part of the treatment.
To continue to the next section go to Convert ASCII to Raster.