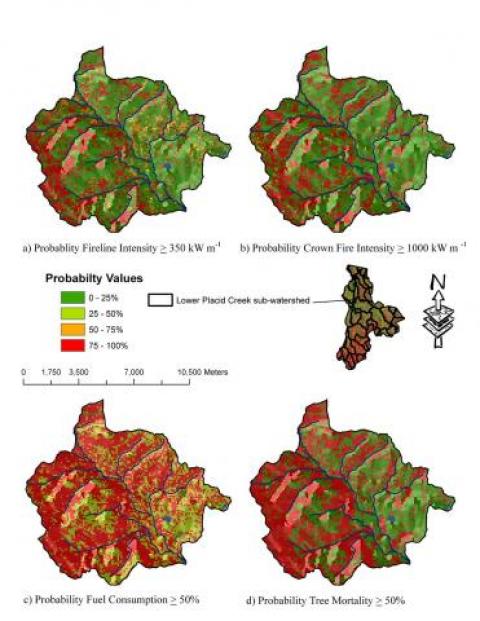
Mapping fire hazard and risk across multiple spatial scales.
This project involves the development of a research computer model called FIREHARM (FIRE HAzard and Risk Model) that computes common measures of fire behavior, fire danger, and fire effects over space to use as variables to portray fire hazard spatially, and then computes fire risk by simulating daily fuel moistures over 18 years to compute fire measures over time. The digital hazard and risk maps can then be used for fire management planning and real-time wildfire operations.
The objective of this study is to develop methods of computing fire hazard and risk that minimize the limitations and drawbacks of previous efforts. The FIREHARM computer model (1) increases consistency across hazard and risk layers, (2) standardize weather inputs, (3) employs a multiple scale analysis into its structure, (4) includes some spatial effects, and (5) expanded the number of fire hazard and risk variables. The audience for this effort is managers and researchers interested in describing and evaluating fire hazard and risk across multiple spatial scales.